What are Amazon Step functions?
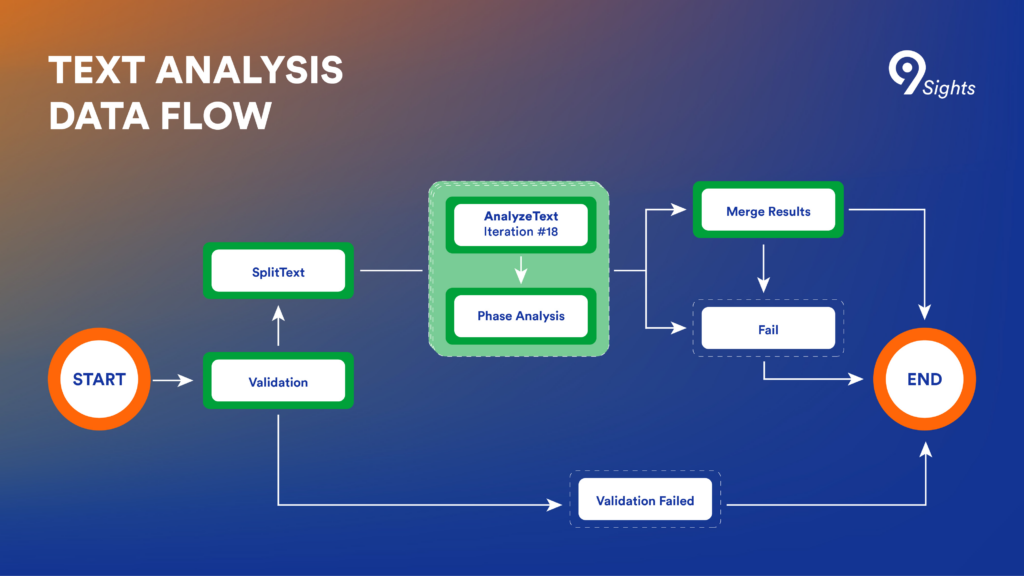
To find out how many words are in each sentence of Queen’s Wikipedia biography, you’ll need to do some common-sense actions: read the text, split it into sentences, count the words, then put back together all the information about each sentence in one single text.
Surely you don’t need automation for that. It’s a straight-forward, simple task. But what if you needed to count all the words in the Wikipedia entries of the Top 100 British bands of all time? This is where Andrei Elefterescu steps in to explain what Amazon Step functions are.
Amazon Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service that helps us integrate multiple AWS services such as Lambda, S3, SNS, and so on to develop various applications. Going back to the Queen example, those steps define a “Step function”.
While it’s easier to visualize as a diagram, Step Functions are written in an AWS proprietary language, which is JSON-based. Of course, Amazon Step functions are much more useful than counting words on a Wikipedia page. The service can be used to process images in S3, ETL (Extract – Transform – Load) processes, machine learning, microservice orchestration, IT and security automation, as well as Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CICD), a process that automates the integration and deployment of code. “Step Function has around 250 integrations with other AWS services and around 11,000 API calls that can be called from it. “In 2016, when they launched, they only had an integration with S3 and 3–4 other services.”
JDK17 brought on pattern matching in a switch. If you want to check an object for its class type, now it’s possible in switch statements too.
Key concepts
Before we delve deeper into how Step functions work, here are some key concepts, as explained by Andrei:
- Workflow is the breakdown of what needs to be done and in what order. It can be built visually, like a diagram, in the very intuitive editor of the Amazon Steps Function. In our example, it’s the mental plan of how we are going to grab the information about the Queen Wikipedia blog article. A good plan needs to include some steps where you validate the inputs and a way to handle errors.
- Triggers are what start the workflow. You can call the API or you can use other methods, such as starting it directly from the AWS console, triggering an S3 event through the SDK, or using the event bridge to start a Lambda function. For our planned mini-Queen automation, we’d just run this through the interface.
- States are the different sequences in the workflow. Step Functions have several types of states, such as task states where a resource can be assigned, choice states where a decision can be made, and check states where a variable can be checked and make the automation behave differently depending on whether it’s true or not. In our mini-automation, the states include grabbing, parsing, and joining the information, but also a validation filter and a choice related to what happens when the automation throws an error.
- Tasks are the actual actions and steps that are performed in each state. A task could be, for example, to split a text into sentences, and another task would be to count the words in each sentence.
- Transitions are links between two steps, and each step is recorded as a transition. For each execution of a lambda, there are three entries: the transition before, the step itself, and the transition after. For the passing of information from one step to another, Amazon has a limit of 250 KB. For our particular case, the information “There are 10 words in the second sentence” must be carried from one step to the next.
- Item execution is the transition from one state to another. The limit per workflow is 25.000 executions. For example, to find out how many words there are in each sentence, there are three executions: one is grabbing the actual sentence, two is getting the numbers, and three is sending those numbers to the following step.
- Express vs Standard Step Functions are two types of workflows. The Standard has a year limit on being active, while the Express has 15 minutes and 100,000 parallel executions. Express workflows are used in web development, while standard Standard workflows are used for larger volumes of data.
- The history of the execution is in the log, which you can easily check in the Step Function dashboard. There is a limit of 100,000 logs per workflow.










